Circulation analysis
The mid-to-high latitude circulation is gradually transformed into a zonal circulation with weak cold air activity. Affected by the Japanese standing wave trough, it is difficult for the subtropical high to move northward, and the ridge line of the subtropical high is maintained at about 15N, and the point of the westward extension ridge is not west of 120E. South China is at the edge of the subtropical high, and there are many short-wave ridges. The relatively southern and stable subtropical high combined with weak cold air activities has established a good large circulation background for the heavy rain in South China. Since the South China Sea summer monsoon has erupted in the early stage, a large amount of high-energy and high-humidity monsoon air flow will be able to move northward, providing sufficient water vapor and energy for subsequent convective activities.
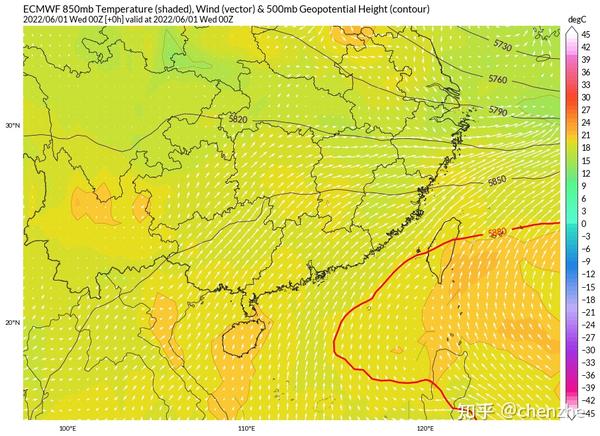
Affected by the short-wave plateau trough, a southwest vortex will be born in the Chongqing area, and it will gradually deepen and develop into a cyclone. The birth of the cyclone accelerated the transport of the Southwest Jet on its southeast side, which further strengthened the water vapor and unstable conditions in South China. After the cyclone was formed, it moved eastward, and it happened that the short-wave trough in Mongolia deepened and moved southward and gradually developed into a cut-off vortex, which drove a significant cold air to the south, and pushed the cyclone to move eastward from the Fujian area as a whole showing a south pressure path.
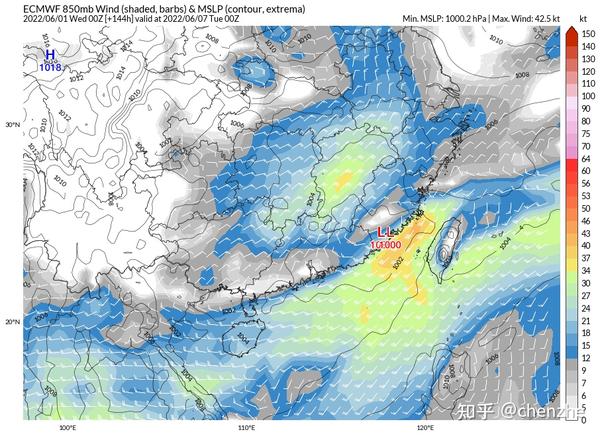
Afterwards, the cold air continued to supplement the south, driving the shear line between the southwest monsoon and the cold air to establish and maintain it along the coast of South China for a long time, and the rain belt retreated to the coast in the south.
Phase 1 6.2-6.5
From the 2nd, the Southwest Jet will be significantly strengthened. From the 2nd to the 4th, the southerly jet stream will be strongest in Guangxi and western Guangdong, and after the 5th, the jet stream will gradually expand eastward and affect the Pearl River Delta and eastern Guangdong. At this moment, the rainstorm will kick off. When the southerly jet stream goes north to the north of Guangxi, due to the large number of hills in the north of Guangxi, there will be terrain friction and cause strong precipitation. Due to the lack of strong uplift conditions, convection in the warm area should be the main factor affecting most of Guangdong at this time. Due to the high thermal intensity and abundant water vapor conditions, short-term heavy rains – short-term heavy rains cannot be ruled out.
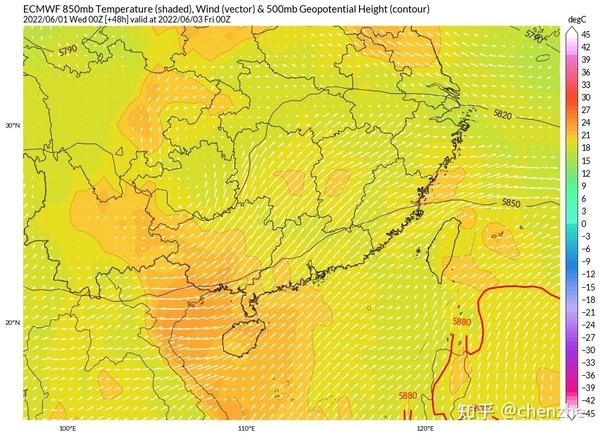
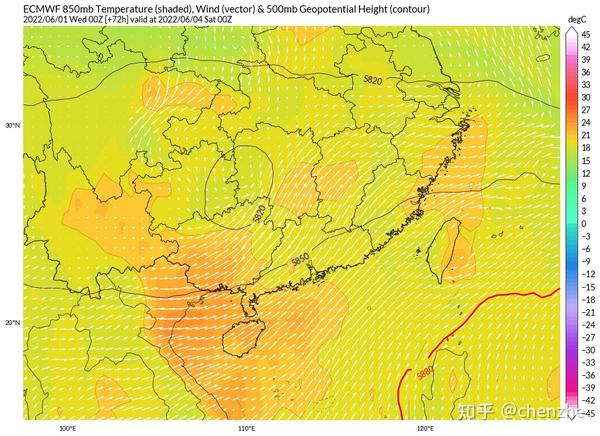
Phase 2 6.6-6.7
This stage of heavy rain will turn to its heyday. The cyclone height developed and became quite deep, and the southerly jet on the south side reached the strongest, and the 850hpa jet core could reach more than 20m/s. The unstable energy, water vapor conditions and dynamic conditions of the atmosphere have all reached the maximum value, which is conducive to the occurrence of heavy rainstorms and extremely heavy rains covering most of South China from Guangxi to Fujian. The shear line precipitation on the east side of the cyclone may form a double rain belt regulation mechanism with the precipitation in the coastal warm area on the south side of the cyclone, further increasing the intensity and scope of the precipitation. The further intrusion of cold air will also cause the release of baroclinic energy, thereby providing further energy for the occurrence of heavy rain. Since this time coincides with the college entrance examination, special attention should be paid to the precipitation.
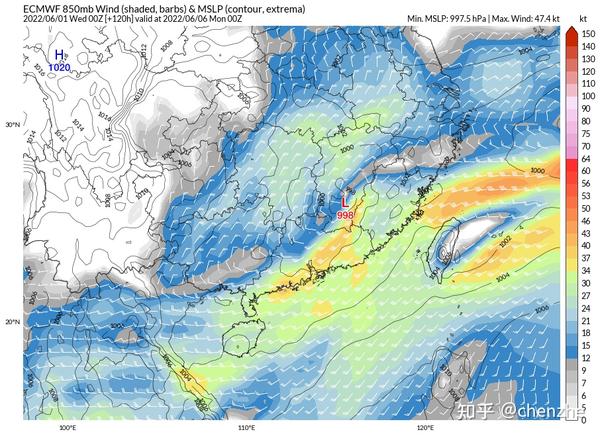
Stage 3 6.8 – Uncertain
Numerical forecasts still disagree on the maintenance of the South China coastal shear after the 8th. It is currently certain that all these changes will have a long maintenance time , which will lead to further retention of the rainbands. Rainfall intensity may be small during this period, but the cumulative total is high.
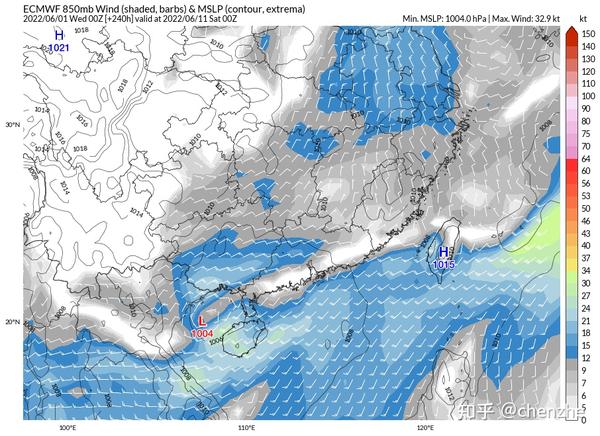
The gap with the dragon boat water in mid-May?
Compared with the Dragon Boat Water in mid-May this time, the rapids are stronger and the thermal conditions are stronger. This also creates two problems:
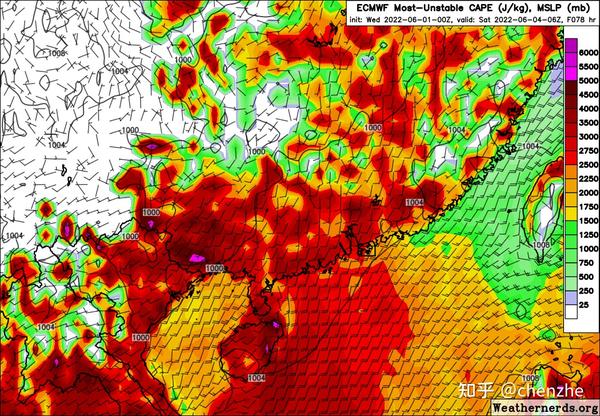
- Stronger thermal conditions are more conducive to the triggering of convection in warm regions. EC believes that the thermal conditions have reached a very strong level around Saturday – the effective potential of convection in a large area in Guangdong and Guangxi can reach 3000J/kg or even higher, which is enough to support strong convection in warm areas, and it is naturally easier to carry The possibility of short-term heavy precipitation and thunderstorms. On the contrary, the thermal conditions of the dragon boat water in mid-May are significantly deficient.
2. The stronger southwest jet stream makes it easier for the warm rain belt to land. During the dragon boat water process in mid-May, the southwest jet stream was weaker than expected, so most of the rainstorms in the warm area fell on the sea surface, and there were not many opportunities to go ashore. However, the rainfall intensity of the ashore sites should not be underestimated. There was an extreme rainstorm of more than 90mm in 30 minutes, which was close to the level of Zhengzhou’s 7.20 heavy rainstorm. This time, due to the stronger southerly jet stream, the possibility of extreme rainbands coming ashore is relatively higher, and it should be more cause for concern.
Uncertainty
- Coupling of boundary layer jets. Boundary layer jet deceleration zone – 850hpa jet acceleration zone double jet coupling is a focus of heavy rain in the warm region of Guangdong. Since global-scale dynamical models are still prone to inaccurate depictions of the boundary layer and the LLJ, this is based on proximity. If there is a double jet coupling, the magnitude of the possible torrential rain should be considered further.
- It is still unknown how long the coastal shear will last in the later period. It is a good thing if the cold air strengthens in the later stage and pushes the shear to the sea, but if the southerly jet stream strengthens again, causing the shear to move north again and causing a large-scale heavy rain, it may not be catastrophic.
in conclusion
The precipitation process in South China in the next few days is extremely extreme. Friends in South China may usher in a large-scale heavy rainstorm and should be prepared. However, the specific rainfall magnitude and rainfall intensity are yet to be determined, but not much weaker. Please pay attention to the latest weather information provided by local weather stations in time to take precautions.
Source: Zhihu www.zhihu.com
Author: chenzhe
[Zhihu Daily] The choice of tens of millions of users, to be a big cow to share new things in the circle of friends.
click to download
This article is reproduced from: http://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/523215072?utm_campaign=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_source=rss&utm_content=title
This site is for inclusion only, and the copyright belongs to the original author.