Summary of Valuation Series Articles
1/7, the valuation is only relatively reasonable
The recent market seems like a nightmare for long-term value investors, especially because the valuation anchor of value investment, Maotai, has collapsed, and the entire valuation system has been shaken.
Long-term investment mainly earns money for the growth of the company, but the volatility of A-share valuations is much higher than the growth in performance. It is like a passenger walking on a train that is fast and slow. It is difficult for investors to distinguish their true speed without knowing their true speed. , How much of the current stock price fluctuation is the fluctuation of performance, and what proportion is the fluctuation of valuation, this is the reason why value investing requires a high margin of safety.
However, the margin of safety you calculate cannot resist the disturbance of fluctuations that exceed your valuation assessment ability. Similar to the relatively rare but powerful disaster of Maotai killing valuation, it reminds us that valuation is only relatively reasonable, not absolutely reasonable.
In other words, valuation is not an objective criterion, but an investor’s subjective perspective on the company’s value judgment.
In other words, valuation is the result of constant changes driven by various factors.
Although the judgment criteria of valuation are subjective, complex and dynamic, in order to roughly evaluate the winning rate, odds and safety margin of an investment, we should try to be as close as possible to the mainstream valuation judgment criteria.
I divide the most common factors that affect valuation in the market into four levels:
Level 1: Company Fundamentals
The second level: the enterprise life cycle
The third level: industry cycle
Level 4: Market Style Cycles
The goal of this article is to systematically sort out the factors that affect the valuation. The previous valuation series articles on the corresponding content have been covered, so each valuation factor will not be discussed in detail. For more articles, you can read it. See my previous article.

2/7. The first level of valuation: company fundamentals
There are many factors related to valuation, mainly: performance growth rate, industry attributes, business model, competitive landscape, and financial risks. If this level can be grasped, most of the valuation conclusions are reliable.
Performance growth
Investors are most familiar with the PEG valuation method. As much as there is a growth rate, they can give as much valuation as possible. This is the level of fundamental valuation.
Growth rate is the most important valuation factor, but the most influential factor is-
Industry attributes
The industry attribute is the most influential factor on the valuation level. Banks usually only have several times of PE, and some TMT industries have dozens of times of PE. Many investors like to question the valuation system of these industries based on PEG, thinking that the market will correct this “mistake”. “valuation.
But there are many reasons behind the formation of the valuation system in this industry. In my article ” What kind of companies can maintain high valuations for a long time? “” 7 premium and discount factors, making the PEG valuation method more accurate and more useful ” and other valuation series articles have analysis. Only the ignorant will be fearless. Due to space limitations, the article will not be discussed.
business model
If it can bring long-term stable cash flow, the market will give a higher valuation. This is the reason why the PE of project-based companies is very low and the valuation of SaaS companies is very high in the computer software industry. This is also a typical case of business model affecting valuation. .
Investors need to continue to pay attention to the business model that the market recognizes and is willing to give a premium to the valuation. My previous business model series articles, such as ” Finding the Best Business Model for A-Shares (1): Using 2C Products to Make 2B Money ” ” Not Good ” The business model is the “accident-prone lot” in investment ” are analyzing this problem.
Competitive Landscape
For two companies with similar conditions, the valuation of the leader can be higher. This is the premium brought by the competitive landscape, which exists in most industries.
Similarly, an industry had a bad competition pattern in the past, often fighting price wars. After mergers and acquisitions, major companies have re-priced their prices, and now they have become better and their performance has increased steadily, which can increase the valuation of related companies.
Financial risk
Some companies that have been suspected of financial fraud for a long time often have their valuations significantly discounted before these doubts are falsified, such as Kang Dexin and Kangmei Pharmaceutical. trap”.
The above are the valuation factors at the level of fundamentals. Among them, the growth rate of performance is a “growth factor”, and the other four are “deterministic factors” , which can explain the valuation of most companies with stable performance at a certain point in time.
However, business operation is a dynamic process, and valuation should also be a dynamic result. The second and third levels are to look at valuation from a developmental and dynamic perspective.
3/7, the second level of valuation: business life cycle
A-shares liked to give small companies high valuations before 2015, and the reason was this life cycle.
Enterprise valuation has a core underlying logic: the valuation of a company is equal to the discount of its future sustainable cash flow.
Assuming a small company with a profit of only 1 million, we can clearly foresee that the future growth cash flow of the company can be discounted to the current market value of 100 billion. In theory, the market can give it a PE of 100,000 times.
This is, of course, an exaggerated assumption, but it represents a way of thinking about valuation. If a company fully demonstrates to the market that it has huge room for growth in the future, it can get a valuation that is much higher than the growth rate.
The most typical example is the Ningde era. When it was just listed, the market value was already 100 billion yuan, and the profit growth rate was similar to that of today, but at that time it could be given more than 100 times, but now it can only be given 20 to 30 times.
Therefore, it is not entirely accurate to say that small companies can give high valuations, and the life cycle does not refer to the age and size of the company when it was founded. Companies of the same size and volume can see that there is a lot of room in the future, that is, companies in the early stage of growth, which can be given a high valuation; it is difficult to see the growth space, which is a mature company in the life cycle, and can only give a relatively low value Valuation.
In general, long-term stock holdings depend on the space, and the total market value is a very important indicator. Thinking should be changed from the stock price coordinate to the market value coordinate. For example, instead of remembering a company’s “EPS0.6, 30 times PE, 18 yuan”, it is “600 million profit, 30 times PE, 18 billion market value”.
In the future, ten times the shares are likely to appear in companies with a market value of less than 10 billion. It is almost impossible for companies with a market value of more than 100 billion. Companies with tens of billions of dollars require strict conditions: or there is a lot of room for industry penetration. Or it is a stage of concentrated and rapid improvement of small companies in large industries, or excellent companies are extremely undervalued in the industry’s predicament.
Of course, in terms of the certainty of growth, mature companies are bigger, so if you invest in large-cap companies with a market value of more than 100 billion, you must find an industry that can see a market value of trillions of dollars. strong company.
4/7, the third level of valuation: industry cycle
The third level of valuation is the industry cycle, and the entire valuation range presents periodic fluctuations.
Many investors think that commodities such as non-ferrous metals, steel, and pigs are cyclical industries. In fact, everything is cyclical, only the difference between strong and weak. Consumer goods such as liquor are growth stocks, and TMT high-end manufacturing industries such as semiconductors and new energy are also growth stocks. , the former is a growth with a particularly long cycle, while the latter is an industry trend-type growth, which lasts for only two or three years, and is more constrained by periodicity.
It can be said that all stocks have growth potential, and all companies are also cyclical, and their stock prices have both “periodic” and “growth”:
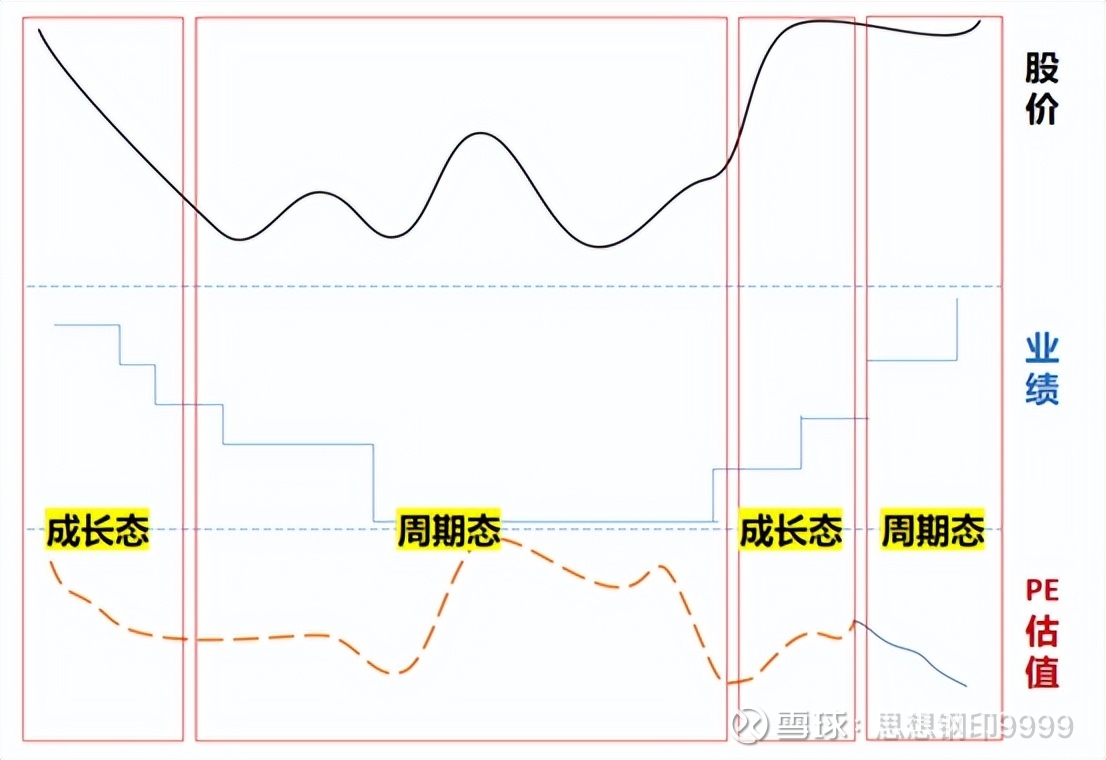
Growth state: Profits and valuations double during periods of rising performance (Davis double-click), while performance and valuations double during periods of downturns (Davis double kills) , what is emphasized here is not the daily changes in valuations themselves, but Overall change in valuation range.
This fluctuation is very understandable, but when the company’s performance declines, it is easily anchored by the previous forecast performance, giving people a cheap feeling. Therefore, when the stock price falls, we must distinguish whether it is the cheap valuation itself or the decline in the valuation range.
Cyclical state: high valuations at lows, low valuations at highs
In the top area and bottom area of the big cycle, there are fluctuations in performance and valuation opposite, that is, the performance is poor but the stock price never falls to rise, and the performance is good, but the stock price never rises to fall.
This kind of valuation fluctuation is also well understood. Generally, experienced investors have this natural awareness when facing a strong cycle industry. But if you are facing the industry trend investment. Since its cycle is often as long as two or three years, investors are likely to ignore the valuation of this cyclical attribute, especially in the prosperous period, thinking that the valuation is cheap under high prosperity, which is wrong to take the downward trend of the industry as the valuation Value is cheap.
From Ping An to Maotai, from Hikvision to the Ningde era, there will be more high-valued and big-eyed guys in the future, who will be prototyped in the downward cycle.
5/7. The fourth level of valuation: market style
The third level of valuation is the market cycle or style cycle . It is different from the ups and downs of the index. It is an internal structural adjustment without considering the changes in the index. Some industries and sectors increase their valuations, and some industries and sector to lower valuations.
Typical market style changes include large and small market capitalization style, growth value style, and track style (that is, the strengthening of plate beta).
The first three levels are all related to the company or industry, and investors will pay more or less attention, but this factor has nothing to do with the company and industry, and the cyclical fluctuations of the capital market itself do not have the significance of the rise and fall of the index. , Similar to the decline of Maotai this time, the valuation of the entire White Horse consumer stock has declined as a whole.
Since this situation rarely occurs, and value investors generally believe that “one minute of macro attention is a waste of one minute”, even experienced investors, by the time they realize this, the stock price has often fallen. a long paragraph.
How to judge the style change? There are many strategies to put forward their own opinions, such as the explanation of the change in the style of small and large market capitalization. When the economy starts to recover from a trough, because the performance and valuation elasticity of small-capitalized companies are stronger, it is easier to rise, and small-capped stocks appear, such as 2019. The market in the first half of the year; when the economy is in recession, large-cap stocks are more resilient due to their strong operating resilience, and large-cap stocks appear, such as in 2020.
But generally speaking, style is a chaotic system, with many influencing factors, it is difficult to predict, and investors can only passively bear it.
More importantly, don’t mistake the money “sent” for style as earned by your own ability. The large-cap stock revolution from 2017 to 2021 changed the previous market’s preference for small-cap stocks. Large-cap stocks with low valuations persisted in their valuation for more than three years. Many long-term investors made several times their profits, thinking that they insisted on long-term value. The result of the investment, as everyone knows, this is the money given to you by the four-year market style.
The money “sent” in style, whether it is a track or a white horse, is temporarily placed with you and will be taken away at any time.
6/7. Three methods of valuation
Let’s first summarize the four levels that affect valuation
The first level: company fundamentals, including performance growth, industry attributes, business model, competitive landscape, and financial risks
The second level: enterprise life cycle, high valuation in the early and growth stages, and decline in valuation after entering the mature stage
The third level: industrial cycle, divided into growth state and cyclical state.
The fourth level: the market style cycle, which belongs to the money that is unreliable, unreliable, and control losses
From the above four levels, three valuation methods can be summarized.
Method 1: From these four levels, comprehensively consider the rationality of the valuation
The best way is of course to comprehensively evaluate the company’s valuation from these four levels, but this requires the establishment of a complete valuation calculation system, and dynamic real-time adjustment, not to mention retail investors, even institutions cannot fully do it.
Method 2: Only consider the reasonableness of relative valuation
Among the four levels of valuation, companies in the same industry have the same impact on the third and fourth levels, and the second dimension is relatively easy to judge. The real difference is the first dimension , so there is A relative valuation method.
First of all, look for a “valuation anchor” in the industry, usually those companies with the most transparent fundamentals, many researchers, and the smallest market expectation difference, we call it “industry valuation anchor”, such as liquor can choose Maotai, battery can choose Choose the Ningde era.
You can acquiesce that the valuation of some targets is reasonable, and then compare and study the differences between the company and the “valuation anchor” at the first and second levels to determine the relatively reasonable valuation of the company.
This method is suitable for companies whose operating status is stable and whose industry attributes are obvious. The advantage is that it is simple and fast, and the valuation is relatively accurate. But the disadvantage is also the word “relative”. You also need to always pay attention to the valuation changes of the “valuation anchor”. Once it changes, the reasonable valuation range of all companies in the sector must be adjusted accordingly.
Method 3: Historical Valuation Method
The idea of the historical valuation method is completely opposite to the third type. It does not consider the fundamental valuation factors, but regards the valuation range of the past one or two years as a reasonable valuation formed by the first level, and focuses on the second and third. , Four levels of change.
For example, for a certain company, the valuation has been in the range of 30 to 50 times in the past period, and the median is 40 times. Then 40 times is the center of the reasonable valuation range by default. Inspect again, will the company’s growth rate increase or decrease in the future? Is the life cycle heading towards high growth or maturity? Is the valuation cycle of the entire sector going up or down? Is the market’s big style cycle up or down?
If these factors are considered comprehensively, it is believed that its valuation range is rising, then we can appropriately move the historical estimate range from 30 to 50 times.
This estimation method is very suitable for industries with rapid changes in operation, but the disadvantage is that it is not quantitative enough.
Therefore, it is more suitable for short- and medium-term investment , and it does not require a particularly accurate valuation.
7/7, the courage to give up
The latter two methods only focus on one of the dimensions and give up the other valuation dimensions.
In actual investment, if you are proficient in simple methods, the effect is often better than complex methods. Therefore, you can also abandon what you can’t grasp, and only focus on what you can grasp.
For bottom-up long-term value investment, only the first and second level factors are grasped; for top-down industrial investors, the second and third level factors are mainly grasped, and the portfolio investment of individual stocks is carried out.
But for this reason, investors must realize that their valuation methods are flawed, and there is a considerable probability of failure. They must fully consider the margin of safety in advance, and have the courage to suspend investment after discovering mistakes.
There are 19 discussions on this topic in Snowball, click to view.
Snowball is an investor’s social network, and smart investors are here.
Click to download Snowball mobile client http://xueqiu.com/xz ]]>
This article is reproduced from: http://xueqiu.com/9277793488/234657090
This site is for inclusion only, and the copyright belongs to the original author.