In 2022, we will reach the bottom of the U-shaped cycle, but at the same time usher in the long-awaited recovery curve. In the job market, Spring River Plumbing Duck Prophet, recruitment recovery is an important sign of industry recovery. The official account of Maimai Talent Think Tank released the “Beaching the Digital Era Talent Migration Report 2023”. Through the analysis of big data on the platform, it will take stock of the most concerned talent trends in 2022 and provide cutting-edge insights for job hunting and recruitment.
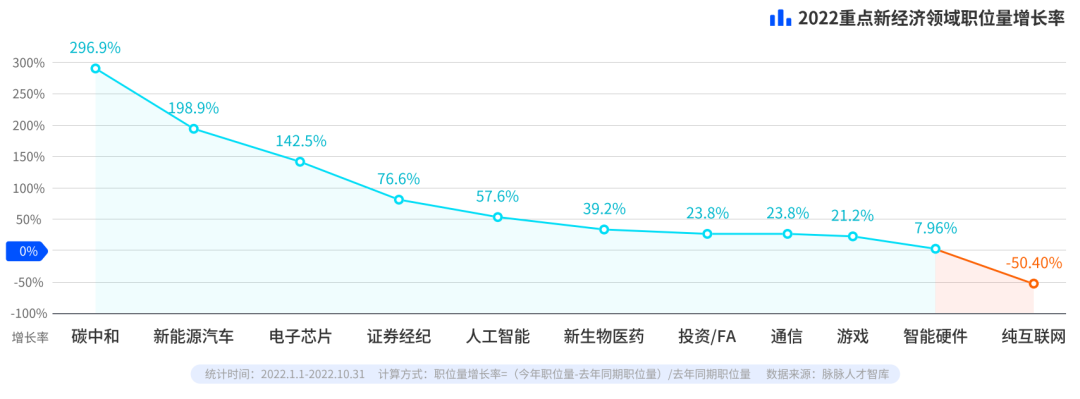
Halve the number of internet jobs and double the number of carbon-neutral jobs
Reduction of recruitment positions: In 2022, the total number of positions recruited by enterprises will decrease by 21.67% year-on-year. The Internet shrinks, and the recruitment of emerging industries expands: the number of pure Internet jobs decreased by 50.4% year-on-year, but the number of jobs in carbon neutral industries increased by 296.9%, the number of jobs in new energy vehicles increased by 198.9%, and the number of jobs in electronic chips volume increased by 142.5%.
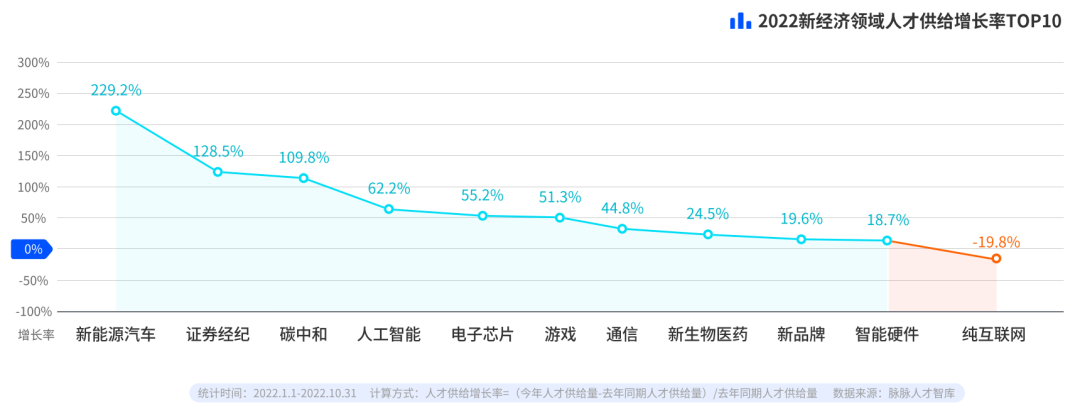
The number of job seekers for new energy vehicles has more than doubled
This year, the number of job seekers in new energy-related industries has increased significantly. In 2022, the number of job seekers in the new energy vehicle industry will increase by 229.2% year-on-year, and the number of job seekers in carbon-neutral industries will increase by 109.8%. And the number of job seekers who want to enter the pure Internet is decreasing. In 2022, the number of pure Internet job seekers will decrease by 19.8% year-on-year.
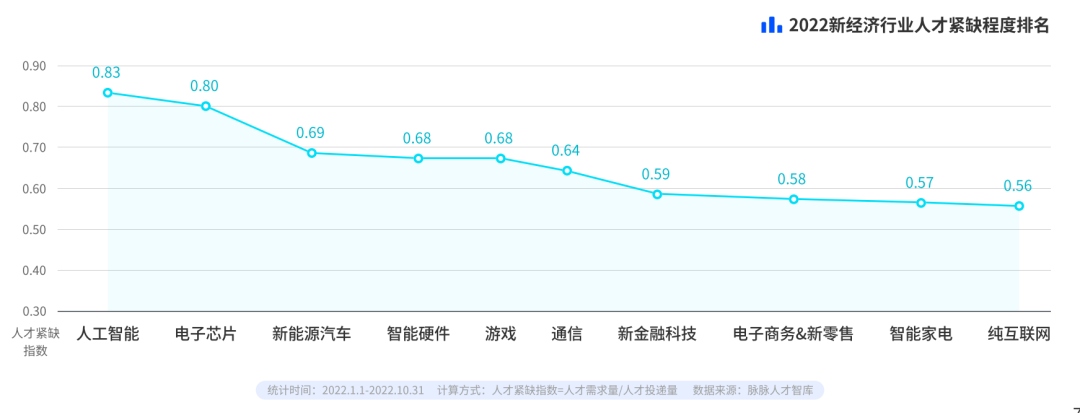
Artificial intelligence will become the most understaffed industry in 2022
In 2022, the most labor-intensive industries will be artificial intelligence, electronic chips and new energy vehicles. The talent shortage index (talent demand/talent delivery) of the artificial intelligence industry is 0.83, and that of electronic chips and new energy vehicles is 0.80 and 0.69, respectively. These new economic fields are still in a state of relative shortage of talents.
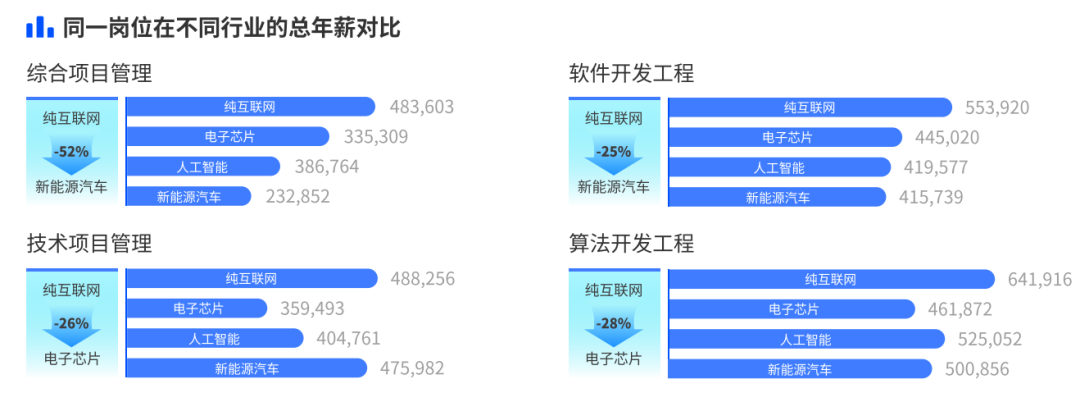
“Salary cut era”: leaving the Internet, there is a salary gap
Salary or prospects? This is a multiple-choice question that Internet people have to face in job-hopping. The data shows that the salary level of the same position in the Internet is still significantly higher than that of emerging industries. For example, software development engineering positions, from pure Internet (average annual salary 553,920 yuan) to new energy vehicles (average annual salary 415,739 yuan), the salary is reduced by about 25%; algorithm development engineering (high-tech) positions, from pure Internet (average annual salary) The average annual salary is 641,916 yuan) to switch to electronic chips (the average annual salary is 461,872 yuan), and the salary is reduced by about 28%.
Note: The above are all pre-tax salaries, and the survey samples are senior professionals (approximately comparable to the P8 of leading Internet companies), and there may be some deviations in the results due to the number of participating companies. Data source: Mercer Consulting
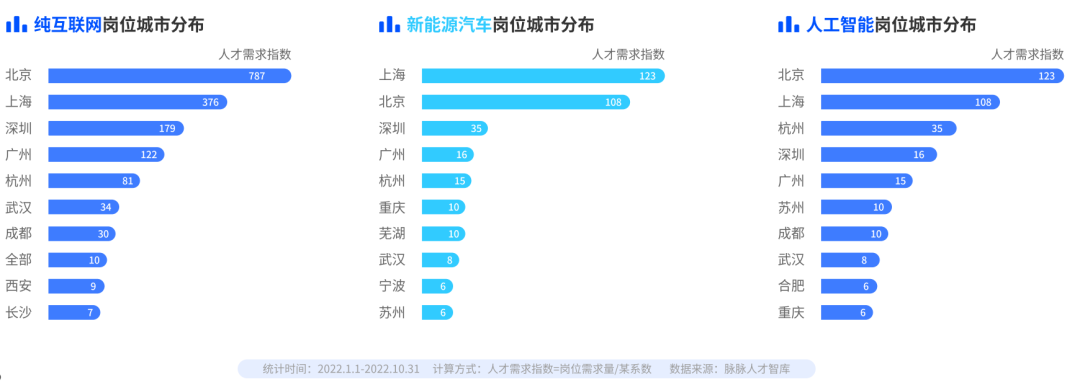
Artificial intelligence looks at Beijing, and new energy vehicles look at Shanghai
Beijing and Shanghai are key cities in the new economy industry. Beijing is the top 1 city with pure Internet and artificial intelligence jobs, and Shanghai is the city with the most jobs in new energy vehicles. Hangzhou is home to artificial intelligence companies such as Alibaba, Hikvision , Dahua, etc., and it also shows a strong demand for talents. In the city distribution of artificial intelligence jobs, Hangzhou ranks third after Beijing and Shanghai.
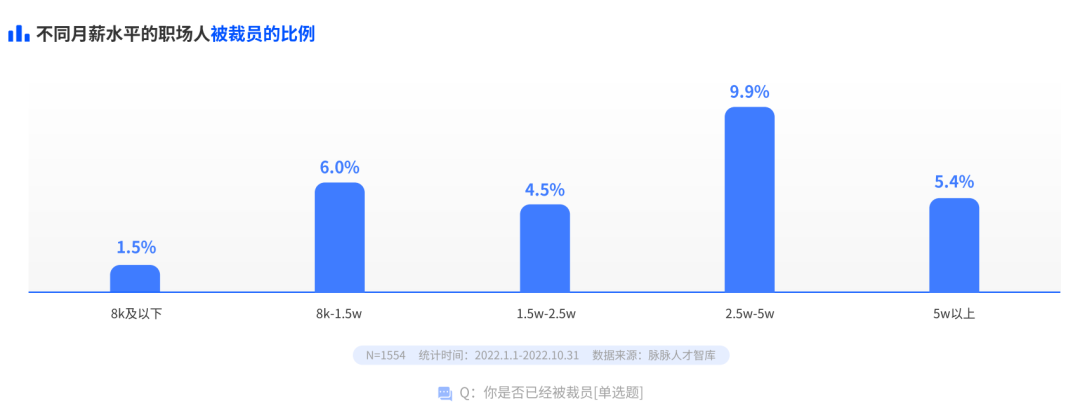
Professionals with a monthly salary of 2.5w-5w have the greatest risk of being laid off
When layoffs strike, “senior migrant workers” bear the greatest risk. Among the interviewed groups, workers with a monthly salary of 2.5w-5w had the largest proportion of layoffs (accounting for about 9.9%); About 1.5% of those with a salary of 8k and below were laid off, and about 6% of those with a monthly salary of 8k to 1.5w were laid off.
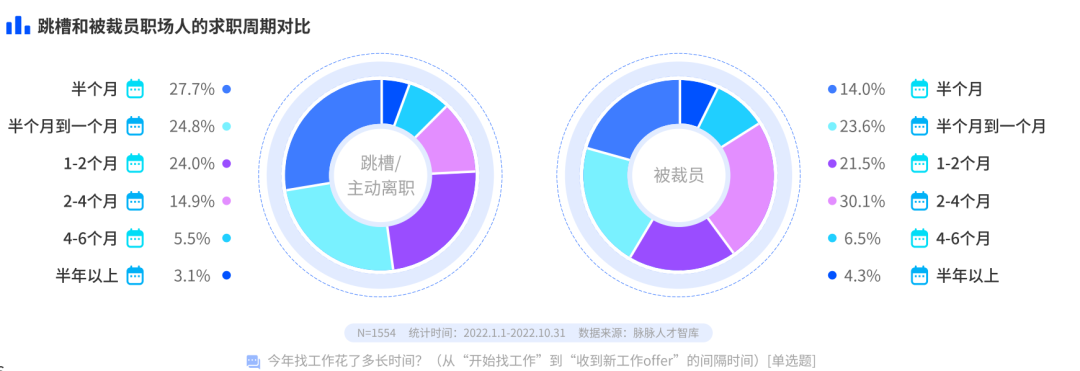
40.9% of the workers who were laid off took more than two months to find a job
Compared with the workers who actively change jobs, the job search cycle of the laid-off workers is longer. (This survey defines the “job search cycle” as the interval from “starting to look for a job” to “receiving a new job offer”). Among the workers who took the initiative to change jobs, more than half (52.5%) found a job within one month; but among the workers who were laid off, most of them took more than a month to find a job, and more than four Cheng (40.9) spent more than two months looking for a job.
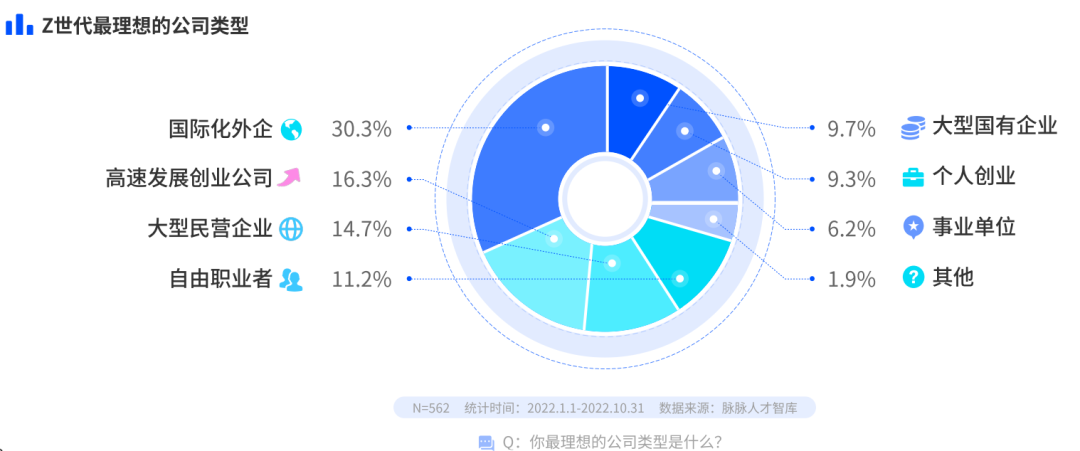
“Internationalized foreign companies” have become the first choice for Generation Z to choose careers
The most ideal type of company for Generation Z is “internationalized foreign companies” (accounting for 30.3%), followed by fast-growing startups (accounting for 16.3%), and the third is “large private enterprises” (14.7%). The proportion of choosing “institution” is the least, and only 6.2% of Generation Z most want to go to a public institution.
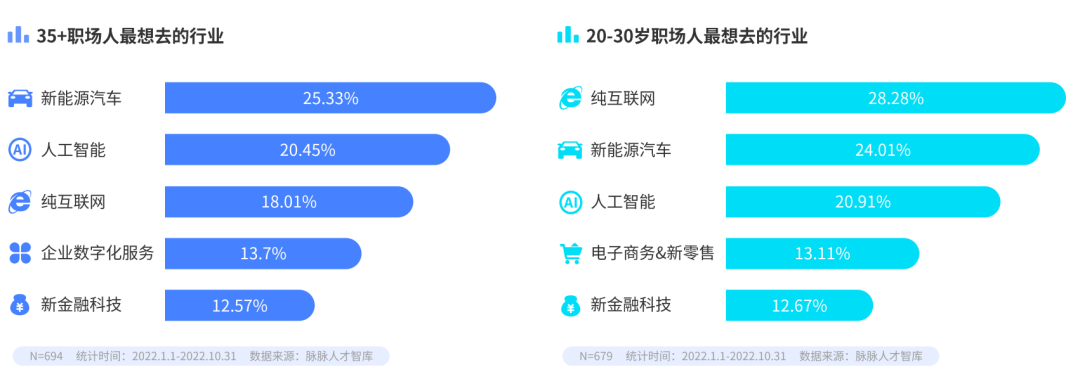
35+ professionals want to go to new industries
Compared with professionals under the age of 30, professionals over 35 years old are more willing to enter new industries. The industries that 35+ workers most want to work in are new energy vehicles (25.3%) and artificial intelligence (20.5%). However, the industry that people aged 20-30 most want to work in is still pure Internet (28.3%).
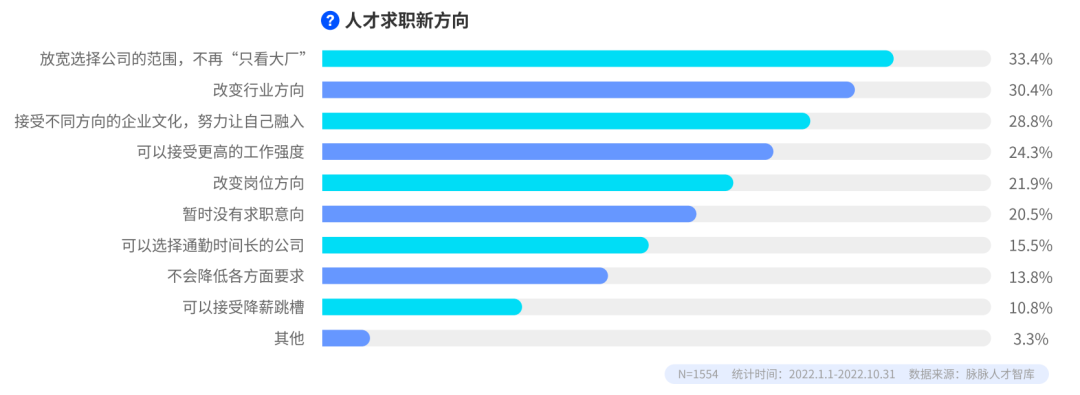
1/3 of people no longer only look at big factories, 1/3 want to change careers
With the increasing pressure of job hunting, professionals are also expanding the scope of job hunting. More than 30% of professionals (33.4%) choose to broaden the scope of company choices and no longer only look at “big companies”; more than 30% of professionals (30.4%) choose to change industries; about 28.8% of professionals can accept corporate culture in different directions change. Among all the ways to broaden the scope of job hunting, “salary cuts and job hopping” are the most unacceptable to professionals.
This article comes from the WeChat public account “Maimai Talent Think Tank” (ID: maimaidata) , 36 Krypton is authorized to publish.
media reports
36Kr Titanium Media Sohu Technology
This article is transferred from: https://readhub.cn/topic/8m6HvK4tu8Q
This site is only for collection, and the copyright belongs to the original author.