1. Overview of engine development system
The domestic engine R&D system process basically comes from the following sources:
1. Pan-Asia Department (General Department): The main reason is that it was the first technology research and development center established by a joint venture, or it has trained many domestic engineers in the field of engines, including UMC and other companies. The flow of these personnel has driven the Pan-Asia engine. The dissemination and application of the R&D system in other OEMs.
2. Acquisition of foreign brands: SAIC (which merged with Nanjing Automobile) acquired Luofu, and at the same time digested and absorbed the development system process of Luofu’s complete vehicle and powertrain. Geely acquired Volvo. After the control has become stronger and stronger in recent years, it has also Gradually introduce Volvo’s engine technology and R&D system.
3. Consulting companies: For example, we cooperate with Austrian AVL Consulting Company, German FEV Company, etc. to help design and follow-up development. Now the hottest brand in the new energy market has a 43% thermal efficiency hybrid special engine developed with the help of AVL Consulting.
I have never seen one that is self-taught, or one that can be developed by itself without the influence of foreign R&D systems.
Second, the engine development stage
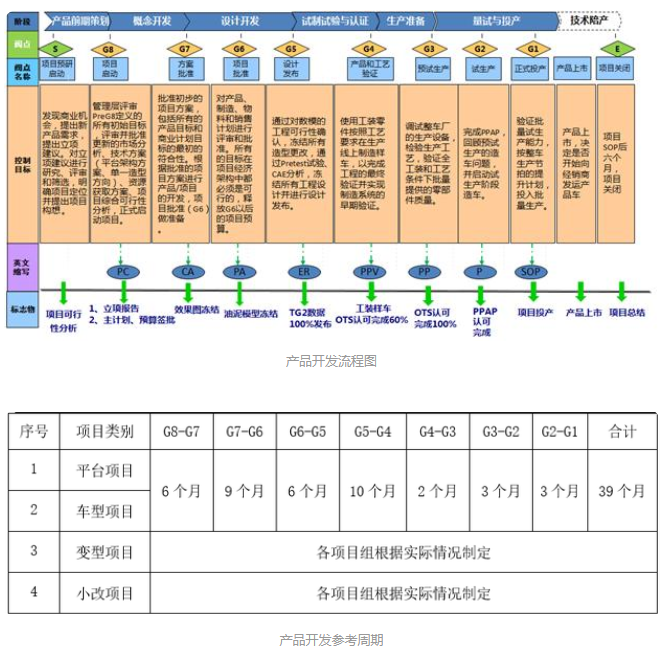
Although everyone’s original research and development system comes from different sources, after all, there is not much new in a century-old industry, and the research and development process is basically dredging and returning to the same destination. The newly developed engine is basically divided into the following five stages:
1. Pre-research stage; 2. Concept design; 3. Development; 4. Verification; 5. Mass production.
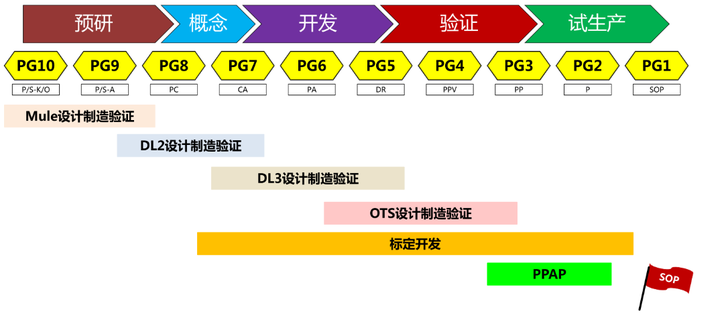
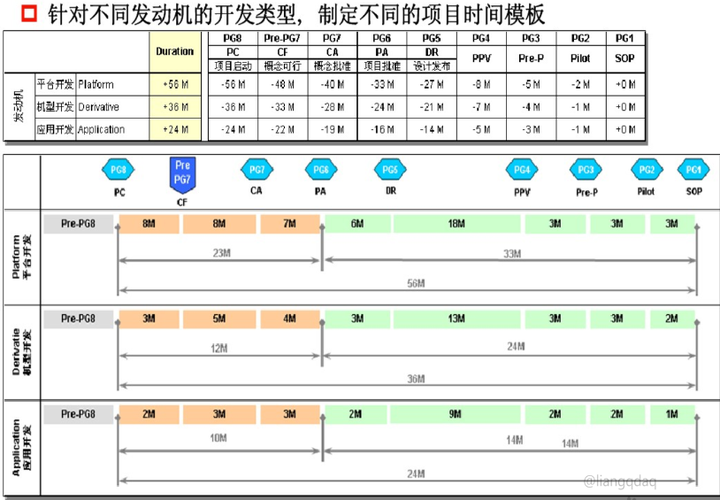
For large modification projects (combustion system changes, such as compression ratio, injectors, etc.) and small modification projects (such as changing small inertia superchargers, etc.), the logic is the same as the new development, but they have relatively base models. , whether it is design, verification, or calibration, there will be relatively less work, so the cycle will be shorter. Usually a new development takes 56 months, while a major modification may take 36 months, while a small modification project or application project generally takes only 24 months, or even less.
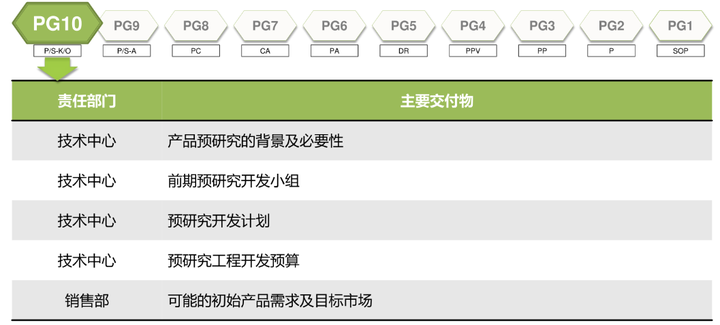
1. Pre-research stage (PG10-PG8)
This stage is actually a long period of time in the OEM. Although there are not many R&D personnel involved in the earlier stage, it is a stage where the development of a brand-new platform engine lays the foundation. Therefore, the preliminary research, benchmarking, technical solutions, and performance indicators are determined. , engine size (need to match the whole vehicle structure), general layout plan (the general layout is not only the parts put together, the most important thing is to consider the production line assembly, vehicle interface matching, etc. in advance), combustion system test (single-cylinder engine As well as multi-cylinder engine), vehicle planning and adaptation, etc., it takes a lot of energy and time to get it. At the same time, a Mule machine is usually made for test verification. Because the engines at this stage are all quick prototypes, the cost is extremely expensive, usually about one million.
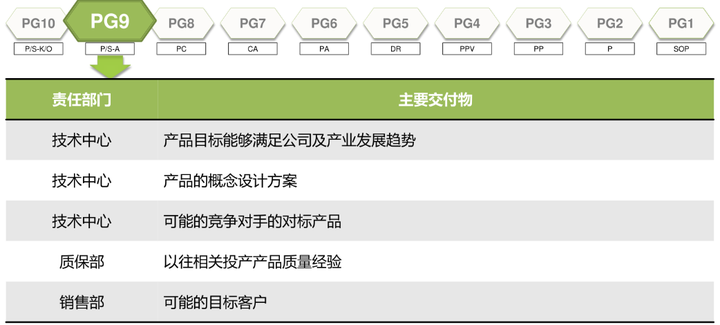
2. Conceptual design (PG8-PG7)
If you can go from pre-research to conceptual design, especially PG8 valve opening (the company approves the project and starts formal research and development), as long as there are no major changes, the engine is usually developed to mass production. So although the PG8 valve point is not decisive for the design, from a project point of view, the PG8 valve point is often symbolic.

In the conceptual design stage, the most important point is the PG7 valve point. Before this valve point, it needs to pass the design verification of the DL2 stage, including the most basic and most important performance, function, and basic calibration work.
Performance contents include: external characteristics, maximum torque, maximum power, universal characteristics, characteristic fuel consumption point, minimum fuel consumption point, miniMAP, idle speed, emissions, etc.
The functional verification mainly includes: the verification of the breathing system (also called the crankcase ventilation system), the verification of the cooling system, and the verification of the lubrication system, which are the three core system verifications, that is, to ensure that the air, water and oil in the engine operation perform their duties well. own work. It also includes the correlation function verification of the intake and exhaust system, the verification of the metal temperature field, and the verification of NVH, etc.
The calibration work mainly includes the calibration of steady-state data, and the core purpose is to support early development work.
At the same time, because the conceptual design locks the performance, the core components related to the performance basically need to lock the supplier, that is, the fixed point.
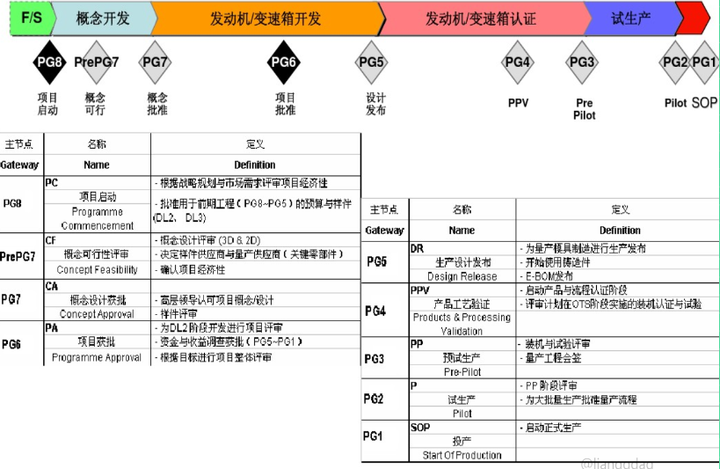
3. Development stage (PG7-PG5)
When the conceptual design review is passed, that is, the performance target is completely locked, and the combustion system is basically no longer adjusted, but the core components of the combustion system are related to the fuel system, cylinder block, cylinder head, crankshaft, piston, and camshaft. The design is also largely locked down.
The most important things in this stage are two tasks: 1. 40% calibration; 2. A large number of comprehensive systematic verifications; and the core goal is 1. Design locking of self-made parts (PG6), supporting the procurement of machining production lines and assembly lines; 2. Other unfixed parts need to be basically verified and fixed at this stage (PG5).

40% of the calibration work mainly includes basic map data, which usually includes calibration content such as inflation model, knock model, boost model, fuel injection pressure, ignition angle, etc., which can support both bench tests and mule cars.
Extensive and comprehensive systematic verification, which includes all functional verifications in the conceptual design stage, and includes a large number of verifications of durability, cold storage, NVH, etc.
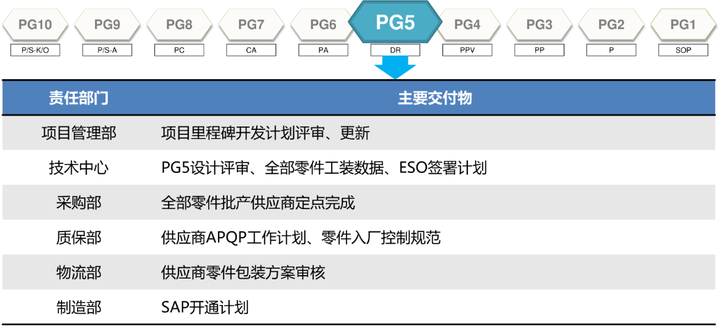
4. Verification (PG5-PG3)
As the name suggests, this stage is verification. If you have no engineering experience, it will be very strange. Why is there verification in the previous stage, the design is locked, and the suppliers are all appointed, so why there is verification.
In fact, when I first entered the company, I also had this question, but I have gradually understood it if I have done manufacturing, especially heavy asset investment. Every investment is huge, not only your own fixed investment, but also the supplier’s fixed investment. If you start a hard mold at the beginning, and pull the supplier to invest in the production line, if you design at an early stage If there is a problem at the stage, if the design needs to be changed, this set of things will be scrapped. Who will bear such a large sunk cost? Therefore, in the face of huge sunk costs in the manufacturing industry, there is gradually a set of effective methods, which is to gradually verify from rapid prototypes to software modules and then to hardware modules (OTS software). Huge fixed investment is lost due to early design changes, changes to the design or process after the verification fails. After the design, process, assembly, etc. are all locked, the hard mold is opened, and then the production line is put into operation, which is a relatively stable development path.

Therefore, this “verification” stage is used to verify the OTS sample. At this time, the status of the sample is the hardware module, the supplier’s production line, or even the factory’s self-made parts. When this stage is completed, it means that the development is completed. The task of the engineering department has been completed, and the next step is to lead the manufacturing and quality assurance intervention.
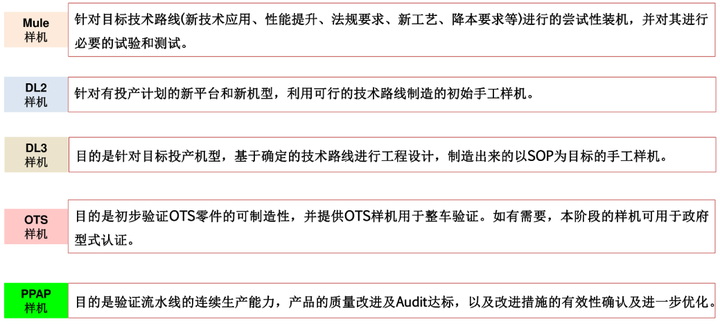
For ease of understanding, the prototype stages and states are listed below, along with their purpose:
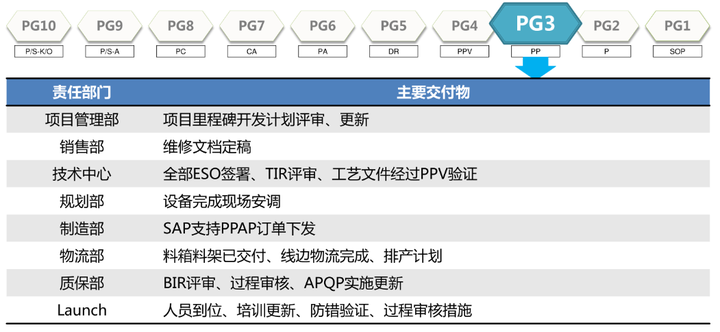
5. Trial production
At this stage, the research and development tasks have basically been completed, and the mass trial production of self-made parts, the commissioning of the assembly line and the production capacity pull have begun.

SOP: start of production, start mass production.
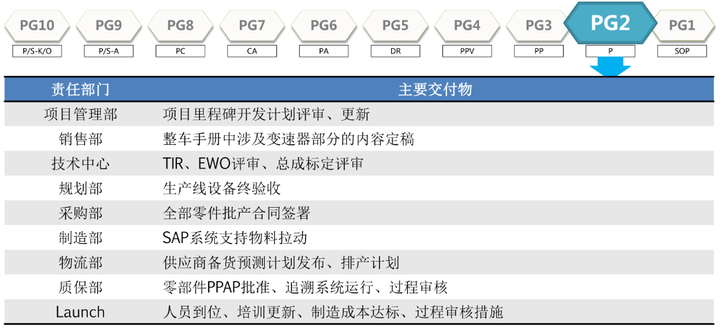
3. The relationship between the engine development process and the vehicle development process
Although the engine development process is independent of the whole vehicle development process, it corresponds to the stages in the whole vehicle development process. The whole vehicle is G10-G1, because the engine development cycle is not only long, but also because it is the power source and the most important Moving parts, so the development will be earlier than the vehicle.
Due to space constraints, this article will not describe the corresponding relationship and logic between the engine development stage and the vehicle development stage in detail.
4. Summary
It can also be seen from this article that engine development is actually quite complicated. The development process is basically equivalent to vehicle development, with a long cycle and heavy investment. This is why in the era of traditional car companies/fuel vehicles, there are three major components, especially the engine. , is the moat of car companies.
It is a pity that many of our own brand car companies have digested and absorbed and established their own R&D system, and have accumulated enough known-how and experienced R&D personnel, but the rapid development of new energy directly Shoot them on the beach.
above.
Source: Zhihu www.zhihu.com
Author: old line
[Zhihu Daily] The choice of tens of millions of users, to be a big cow to share new things in the circle of friends.
click to download
There are 8 more answers to this question, see all.
Further reading:
What is the current R&D capability of domestic operating systems?
This article is reproduced from: http://www.zhihu.com/question/538008768/answer/2573083387?utm_campaign=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_source=rss&utm_content=title
This site is for inclusion only, and the copyright belongs to the original author.