I once received a consultation from a friend and took a photo of the back of my hand under the setting sun. When I sent it to me on WeChat, the description was quite poetic:
“I have never paid attention to the back of my hand. I was driving across the bridge after work that day, and it was a bit blocked. I listened to the song and looked around. I suddenly found a bulge on the back of my hand, and the setting sun was shining on it. At first I thought it was because of my dazzling eyes, but after a closer look, there was indeed a bump . It’s been a few days, and this bag is still there, what do you think it is?”
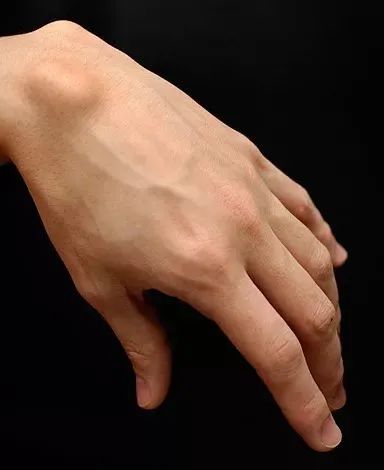
Ganglion cyst | Wikimedia Commons
Judging from the location, shape, size, and symptoms of the lump on the photo, nine out of ten it should be a ganglion cyst . The rigorous thinking of the medical students told me: To diagnose whether the bulge on the back of a friend’s hand is a ganglion cyst, it should also be differentiated from an infectious paraganglion cyst , subcutaneous lipoma or other masses .
In the spirit of “no treatment without accurate assessment”, I replied to her: “It may be a ganglion cyst. It’s not a big problem. Let’s take a look in person when you have time.”
That night, this friend sent me a WeChat message again: “After taking a shower at night, I felt very unsteady and touched this new friend on the body . When I touched it, I felt that the cyst suddenly burst, and then the bulge on the back of the hand disappeared. ”
After that, I took a photo and sent it to me: “Look, is the back of your hand flat?” This result told me that the judgment at that time was correct. The bulge on the back of her hand was indeed a “ganglion cyst”.
What is a ganglion cyst?
Like the scabbard of a sword, a tendon sheath is a sheath that wraps around a tendon. The tendon sheath is divided into two layers, the outer layer is a fibrous sheath, and the inner layer is a synovial membrane that secretes synovial fluid. During muscle movement, synovial fluid lubricates the sliding of the tendon.
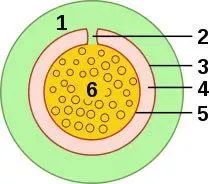
Tendon Sheath Cross Section 1. Tendon fibrous sheath 2. Mesentery 3. Parietal layer of synovial sheath 4. Synovial cavity 5. Visceral layer of synovial sheath 6. Tendon | Wikipedia
Ganglion cyst is composed of cyst wall, pedicle and cyst fluid. The cyst wall is dense fibrous connective tissue, and the cyst fluid is colorless transparent peptone mucus. A ganglion cyst is like a small balloon filled with water , and the inflatable mouth is its “pedicle”, leading to the joint cavity.
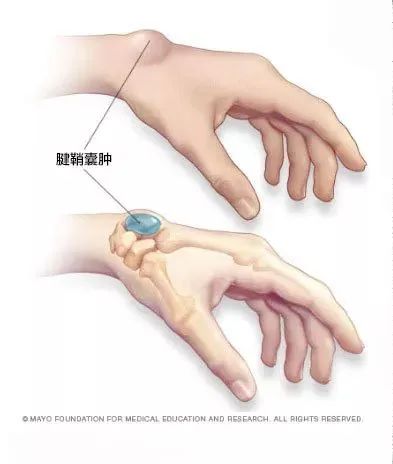
Ganglion Cyst | Literature [3]
The formation of a ganglion cyst is a long-term process that is usually asymptomatic and goes unnoticed. It is not detected until it protrudes from the surface of the skin.
The cause of its formation is still inconclusive, the currently recognized view is that: ganglion cyst is a degenerative cyst. Trauma, strain and ligament laxity can lead to a series of pathological changes of the tendon sheath: increased production of synovial fluid, decreased discharge or absorption, bulging of the tendon sheath, accumulation of synovial fluid, and formation of cysts .
Ganglion cysts are more common in people with active hands
Ganglion cysts generally occur in areas of high mobility, such as the back of the wrist, the inside of the wrist, the joints of the fingers, and the instep . These places are superficial and cysts are easy to spot. When a superficial ganglion cyst bulges over the skin surface, the bulge appears to be well-defined, smooth in appearance and can be pushed gently. Other ganglion cysts occur in the elbows, knees, hips, and even the temporomandibular joint.
Like tenosynovitis, ganglion cysts are also more common in people who use more hand movements, especially those who have more wrist flexion and extension activities – keyboard players, piano players, guitar players, and new mothers who often pump milk and hold babies. Ganglion cysts can occur in all hands.
What should I do if a ganglion cyst occurs?
When sharing various experiences and experiences about “ganglion cyst”, people often say: “This is a small matter, just press it yourself.” This is not desirable!
At present, conservative treatment is still the preferred method for the treatment of ganglion cysts .
After a ganglion cyst is diagnosed in an orthopaedic or hand surgery clinic, the doctor may easily crush the cyst. Self-compression is not recommended until a diagnosis is made. If the bump on the hand is not a ganglion cyst but a malignant mass, the consequences of pressing are unimaginable. The pressing of the cyst is not like pinching a bubble, and requires certain techniques and skills.

Figure | Figure Worm Creative
Moreover, after the ganglion cyst is pinched and ruptured, the cyst wall and pedicle are still there, and the synovial fluid is still secreted . If the living and working habits that lead to ganglion cysts are not improved, it is easy to recur .
Sometimes ganglion cysts go away without treatment, but they are often prone to recurrence.
How to avoid recurrence?
Doctors usually recommend surgical treatment, including open surgery and arthroscopic surgery . Surgery can completely remove the pedicle of the cyst, reducing the recurrence rate.
what can I do:
-
Adjust lifestyle and work habits that can lead to ganglion cysts.
-
Use a wrist rest to support your wrist when using the keyboard and mouse, or replace a set of ergonomic devices.
-
When practicing musical instruments, pay attention to your posture and combine work and rest.
-
New mothers can use a feeding pillow when breastfeeding; avoid holding the baby for a long time, or use a sling, waist stool, etc.; and, choose a suitable electric breast pump.
It should be noted that not all masses are ganglion cysts. When a surface mass is found , it is recommended to go to the hospital for treatment . The doctor will make a diagnosis through the evaluation of the manipulation and the judgment of the symptoms. If necessary, there will be color Doppler ultrasound, nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray, CT and pathological examination to clarify or differentiate the diagnosis.
references
[1]. Hu Fei, Shang Xifu, Kong Rong, Fang Shiyuan, Tong Yuan, Diagnosis and surgical treatment of soft tissue masses in the wrist, [J], Chinese Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery. 2007(02)
[2]. Jiang Liya, Zhang Jia. Treatment of ganglion cyst on the back of the wrist: history and progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 2016(06)
[3]. https://ift.tt/ZS4nefR
Author: april sometimes
Editor: Mu Yi Yang Yang, Dongfeng
an AI
People with obsessive-compulsive disorder have a ganglion cyst, so take it easy!
This article is from Nutshell and may not be reproduced without authorization.
If necessary, please contact [email protected]

This article is reproduced from: http://www.guokr.com/article/462406/
This site is for inclusion only, and the copyright belongs to the original author.