I finished talking about some basic concepts of bankruptcy and reorganization of listed companies last time. Today, I will focus on how to analyze the overall debt level of listed companies and judge the general direction of future reorganization based on the debt level.
We all know that liabilities and assets cannot be analyzed separately. If you look at assets without liabilities, even many assets may be insolvent; if you look at liabilities without assets, it is not easy to judge the true liabilities of an enterprise. A reasonable way is to Combine the two. In the process of bankruptcy and reorganization, the most important thing is the recruitment of investors and the formulation of the final reorganization plan. The reorganization plan is also the final win-win result obtained by the joint coordination of investors, listed companies and creditors. In the reorganization plan , the most notable ones are the debt repayment plan and the equity change plan.
The reorganization plan usually makes a clear division of the creditor’s rights, and the creditor’s rights are roughly divided into the following two categories, namely, the creditor’s rights with high repayment ratio and the creditor’s rights with low repayment ratio:
1. Claims with high repayment ratio
This name is not very precise and belongs to my personal creation. The high repayment ratio of debt is relatively speaking. This part mainly includes several types of claims, namely bankruptcy expenses, common debts, employee claims and small parts of ordinary creditors. In the balance sheet, we can observe short-term borrowings, long-term borrowings, taxes payable, employee compensation payable, and non-current liabilities due within one year. The reason why the repayment ratio of this part of the creditor’s rights is high is actually relatively simple. The bankruptcy costs mainly include the litigation costs of bankruptcy cases, the costs of bankruptcy administrators, and the service fees of audit institutions and intermediaries. Expenses, if you don’t feed the cows, how will the cows run? Common debts are wages and social security expenses incurred in the continued operation of the enterprise; employee claims are very simple. In order to maintain stability, the wages owed to employees must be repaid in full, and secured claims with mortgages. This part of financial institutions accounts for a relatively high proportion. Usually, the final repayment ratio of this part of the claims is also relatively high (may be realized in the future).
2. Claims with low repayment ratio
The holders of this part of the creditor’s rights are ordinary creditors. As the name suggests, they are ordinary. The creditor’s rights they hold are not mortgaged. It may be the project payment, the supplier’s supply payment, or the arrears of rent, fees, and current payments. Wait, this part of the creditor’s rights will usually be repaid with a certain discount. After the small part is paid off directly, part of the remaining creditor’s rights will be discounted and part of the debt will be retained.
In practice, how do we distinguish the quality of debt? In fact, it is relatively simple. In the balance sheet, our focus should be on financial liabilities. If the proportion of financial liabilities in the liability structure of the bankruptcy reorganization subject is relatively high, then the probability of successful corporate reorganization will be relatively large. . The reason is relatively clear. Under the circumstance that investors are interested in entering the market and the company’s future operating environment may be improved, financial institutions are usually willing to accept a package of “debt retention” solutions. The retention period is 3-5 years. Institutions can continue to enjoy a certain amount of interest, and there will be no substantial bad debts and losses on the books of financial institutions. In the future, when the fundamentals of the company reverse, they can still be paid in full. Even if they are unwilling to keep debts, financial institutions can sell their debts to asset management companies at a discount, making the asset management company a new creditor of the company and replacing the role of the original financial institution in the subsequent company reorganization process (typical The case is the debt settlement plan of $*ST Chengxing (SH600078)$ , Jiangsu Assets acquired most of the debts of financial institutions, and finally completed debt restructuring and exemption through debt replacement), so judging the debt ratio of financial institutions is a judgment The core point of debt quality, let’s take a few examples of companies currently in the process of restructuring:
On June 21, $*ST Security Control (SZ300370)$ issued an announcement, announcing the equity adjustment plan of the reorganization plan. The equity adjustment mainly includes two parts, namely: pre-reorganization investors and shareholders implement debt waiver for the company , a total of 270 million yuan of debts of the company were exempted; in addition, the capital reserve was converted into share capital at the ratio of 6.48 shares for every 10 shares, and 60% of the transferred part was used to introduce investors, and the investors issued funds to transfer the capital. Part of the equity, this part of the funds is used for the company to pay the reorganization costs, pay off various debts, supplement the working capital, and the other 40% is used to offset debts with shares.
Investors basically lock in the cost price of entering the company in this link, which is the result of a multi-party game. Listed companies hope that the final equity transfer price will be as high as possible, so that the company can have more ammunition to replenish liquidity while paying off debts; investors hope to reduce costs, it is very simple, only cheap purchases can be credited in the future earn more. In the past, when there were loopholes in supervision, investors of listed companies often signed a cabbage price early to lock the entry price, which usually eroded the interests of minority shareholders. If the old shareholders are not transferred, the price of the rights and interests held by the old shareholders will be reduced. Therefore, in February this year, the state issued new regulations on reorganization to protect small and medium investors. Article 25 stipulates:
The pricing of the relevant transferred shares shall be reasonable and fair, and shall not harm the interests of small and medium investors. If the price of the relevant transferred shares is lower than 80% of the closing price of the company’s shares on the day when the investment agreement is signed, the listed company or the manager shall hire a financial consultant to issue special opinions and disclose them.
Regarding this clause, I have conducted in-depth communication and exchanges with the bankruptcy administrator friends of the law firm. According to their communication with the court , the price on the signing date of the investment agreement can be the price of the day or the price of a range. , such as the 30-day average price or the 60-day average price, on the one hand, it prevents the company’s stock price from skyrocketing during the reorganization process and the problem of excessive investor intervention costs, and also prevents large shareholders and investors from privately negotiating pricing that damages the interests of small and medium shareholders. situation occurs.
Going back to st security control, according to the 2021 annual report, the company’s current liabilities total 2.44 billion, non-current liabilities total 300 million, and liabilities total 2.74 billion. Among the current liabilities, short-term borrowings are 880 million yuan, mainly including about 250 million yuan of secured loans and 640 million yuan of guaranteed loans (credit types). These 800 million yuan are basically liabilities of financial institutions.
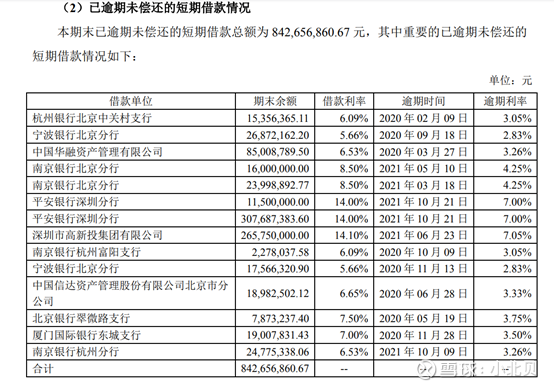
Among operating liabilities, accounts payable amounted to approximately RMB 494 million, and other payables amounted to approximately RMB 630 million. Interest payable on loans from financial institutions is 220 million yuan, totaling about 1.3 billion yuan; long-term loans are 230 million yuan from financial institutions.
It can be seen that the company’s overall liability structure is very clear. The total borrowings of financial institutions are about 1.3 billion, and the operating payables are about 1.1 billion, which constitute the overall liabilities. 550 million in cash plus 270 million in debt waived by institutions, the total remaining balance of financial institution loans is 1 billion yuan, and operating accounts are about 1 billion yuan. Part of the cash that is converted into equity is used to repay operating accounts payable. The increased share capital can be used to repay the debt of about 500 million yuan with shares.
The overall plan is simple and clear after calculation. Under this plan, investors use a relatively small amount of capital to minimize the debt ratio of the company and reduce the burden of the company. The retention of debt by traditional financial institutions can reduce the short-term cash of the company. Due to the pressure of current flow, the payment payable by the business type can reduce the overall debt level of the company. After the financial bath, the investors can resolve the survival risk of the company with a small investment. The possibility that this plan can finally be passed is very high.
Take a recent popular stock $*ST Botian (SH603603)$ as an example. I saw an article on Snowball before that it would be very difficult to analyze the reorganization of Botian with tens of billions of debts. With the ideas just sorted out, let’s briefly analyze the debt situation of Poten Environment.
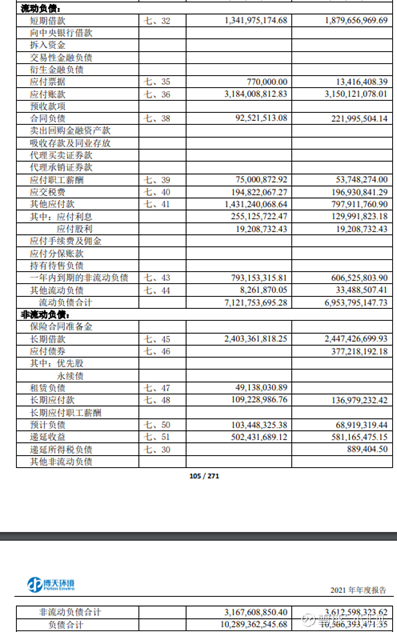
It can be seen that among the existing tens of billions of liabilities, there are short-term loans of 1.3 billion yuan, long-term loans of 2.4 billion yuan, bonds payable of 380 million yuan, financial liabilities of other payables of about 500 million yuan, and non-current due within one year. Debt is 800 million yuan, and financial loans total about 5.4 billion yuan. Accounts payable is 3.2 billion yuan, and other payables are 1.4 billion yuan (of which 900 million yuan) are operating liabilities. This part of the debt is obligated to pay off. In addition, deferred income and estimated liabilities of more than 600 million yuan are not expected to be repaid in the short term. debt impact.
Short-term loans, long-term loans and bonds payable total about 5.4 billion. These claims are all claims of financial institutions. According to the ideas we just analyzed, most of these claims will choose to keep debts in future debt repayment plans. Many of the short-term borrowings have been overdue for more than one year, and the financial institutions have already started to make bad debts and carry out corresponding impairment treatment. Therefore, there is great hope for a plan to retain debts.
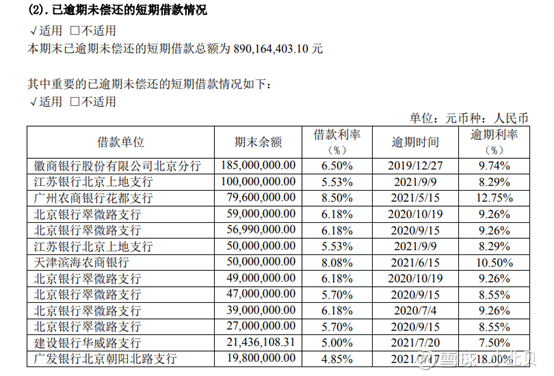
For operating liabilities of 4 billion yuan, the company needs to realize the repayment according to the equity adjustment plan. The company estimates that the capital reserve that can be used for conversion is about 600 million, and the share capital after conversion is about 1 billion shares, and the number of conversions is about 6 billion shares.
For the transferred part, one part is directly transferred by the investor, and the other part is given to the original creditor with shares to offset the debt. Creditors with operating liabilities can still choose to keep the debt or directly repay the debt. For details, please refer to *st Chengxing’s creditor’s rights The settlement agreement stipulates:

The actual operating liabilities that need to be repaid in the short term are about 2 billion, and the cash obtained from the conversion and the repayment of debts with shares can cover this part of the creditor’s rights. Therefore, the burden of debts of tens of billions of dollars seems scary. At the same time, it is also possible to clear the cloud and see the sun. At the same time as the financial bath, it is possible for the company to transform into the popular hydrogen energy and salt lake lithium extraction track while maintaining the original BOT water environment treatment main business smoothly.
To sum up, to judge the quality of the overall liabilities of a listed company in bankruptcy and reorganization, my usual practice is to first classify the debts. First, we need to focus on financial liabilities. If this part of the liabilities accounts for 40%-50% of the overall debt ratio or even If it is higher, then subsequent reorganization investors can obtain control over the company at a lower cost; secondly, the proportion of operating liabilities, the length of the account period, and whether it is a current payment from a related party will have an impact on future debt repayment. ; Finally, whether some liabilities with a high repayment ratio, such as employee salaries and taxes payable, account for a higher proportion, because such liabilities are claims with very high priority in repayment (the company needs to raise cash to pay).
In the follow-up, we will analyze the assets of the reorganized company. How to judge the overall quality of the assets of the reorganized enterprise? Stay tuned. (Original is not easy, thank you for your support ![]() )
)
There are 68 discussions on this topic in Snowball, click to view.
Snowball is an investor’s social network, and smart investors are here.
Click to download Snowball mobile client http://xueqiu.com/xz ]]>
This article is reproduced from: http://xueqiu.com/3949100611/223482719
This site is for inclusion only, and the copyright belongs to the original author.